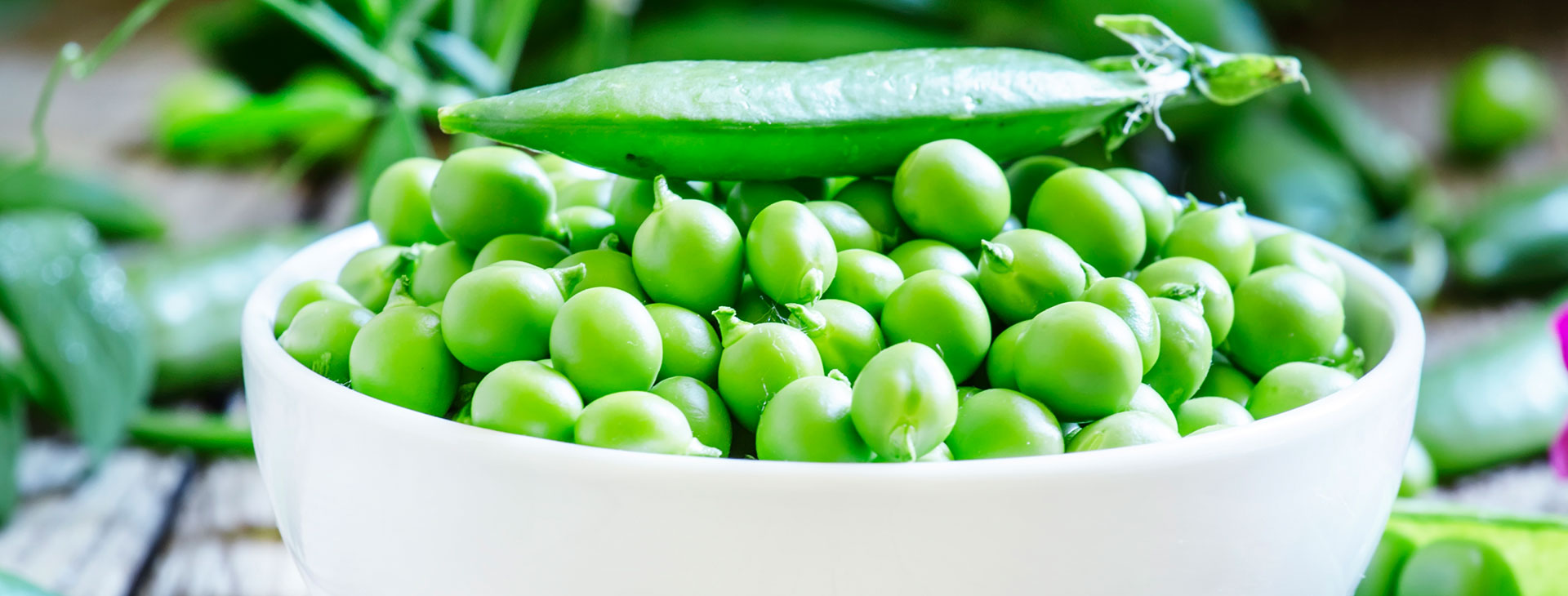
Bright green peas provide essential protein, fiber, and vitamins.
Green peas are more than just a side dish on your plate—they are a powerhouse of nutrients, a versatile ingredient in global cuisines, and an excellent addition to any healthy diet. From their vibrant green color to their sweet, tender flavor, green peas pack protein, fiber, and essential vitamins that make them perfect for vegetarians, weight-watchers, and anyone seeking a nutritious meal. This article explores everything you need to know about green peas, including nutrition, health benefits, culinary uses, and practical tips for storage and preparation.
Biographic Table of Green Peas
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pisum sativum |
| Type | Legume |
| Common Varieties | Garden peas, snow peas, sugar snap peas |
| Nutrients | Protein, fiber, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin K, iron, magnesium, potassium |
| Popular In | Soups, salads, curries, stir-fries, frozen dishes |
| Origin | Middle East, cultivated globally |
Nutritional Profile of Green Peas
Vitamins and Minerals in Green Peas
Green peas are loaded with essential vitamins and minerals. One cup (160g) of cooked green peas provides around 8.6g of protein, 9g of fiber, 62 calories, and key vitamins like Vitamin A (34% DV), Vitamin C (22% DV), and Vitamin K (48% DV). The minerals include iron, magnesium, and potassium, which play critical roles in heart health, muscle function, and bone strength. Including green peas in your diet can help fill nutritional gaps, especially for those who follow a plant-based lifestyle.
Protein and Fiber Content
One of the standout features of green peas is their high protein and fiber content, making them a rare legume that satisfies both. Protein helps repair tissues, build muscle, and maintain energy, while fiber supports digestion, promotes a feeling of fullness, and helps control blood sugar levels. For vegetarians or people looking for plant-based protein sources, green peas are an excellent choice.
Low Calorie and Glycemic Benefits
Green peas are low in calories yet high in nutrients. With just 62 calories per cup, they are ideal for weight-conscious individuals. Additionally, the combination of fiber and protein helps regulate blood sugar levels, making green peas a diabetic-friendly option. Unlike starchy vegetables, they have a low glycemic index, providing steady energy without spikes in blood sugar.
Health Benefits of Green Peas
Boosts Immunity
Green peas are rich in Vitamin C and antioxidants, which strengthen the immune system and help your body fight infections. Regular consumption can support overall health and improve your body’s resilience against seasonal illnesses. Nutritionist Dr. Emily Carter notes, “Adding green peas to your daily meals enhances immunity and provides protective phytonutrients.”
Supports Heart Health
The fiber, potassium, and phytonutrients in green peas support cardiovascular health. Fiber helps reduce LDL cholesterol, potassium balances blood pressure, and antioxidants reduce inflammation in the arteries. Including green peas in salads, soups, or stir-fries can contribute to long-term heart health.
Aids Digestion and Weight Management
The high fiber content promotes healthy digestion by feeding beneficial gut bacteria and preventing constipation. Additionally, fiber and protein together create satiety, helping you control your appetite and manage weight more effectively. People trying intermittent fasting or calorie-controlled diets can particularly benefit from including green peas in meals.
Promotes Eye and Skin Health
Green peas contain Vitamin A and lutein, which support healthy vision and protect against age-related eye conditions. Antioxidants in green peas also maintain skin elasticity and prevent premature aging, making them a beauty-friendly food.
Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
For people with diabetes, green peas help stabilize blood sugar levels. Fiber slows down glucose absorption, while protein ensures a more gradual release of energy. Studies have shown that regular consumption of legumes like green peas can reduce the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Culinary Uses of Green Peas
Cooking Methods
Green peas are incredibly versatile. You can boil, steam, stir-fry, or roast them. Steaming preserves most nutrients, while stir-frying with a small amount of olive oil enhances flavor without adding excessive calories. Roasting green peas creates a crunchy snack rich in protein and fiber.
Recipes and Pairings
Green peas can be integrated into various recipes. For example, a simple pea soup with onions and mint makes a refreshing meal. They also pair well with rice, lentils, pasta, and even mashed potatoes. In Indian cuisine, green peas are often added to curries and pulao, while in Western dishes, they appear in salads, risottos, and pasta dishes.
Frozen vs Fresh Green Peas
| Type | Nutritional Value | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh | Slightly higher in Vitamin C, natural flavor | Salads, quick cooking |
| Frozen | Retains most nutrients if frozen soon after harvest | Soups, stir-fries, long-term storage |
Buying, Storing, and Preparing Green Peas
How to Choose Fresh Peas
Look for bright green, firm pods. Avoid pods that appear yellow, shriveled, or have black spots. Fresh peas should snap easily when bent. High-quality peas are sweet, tender, and full of flavor.
Storage Tips
Store fresh peas in the refrigerator in a perforated plastic bag for up to 3–5 days. For longer storage, blanch and freeze them to preserve nutrients. Avoid leaving peas at room temperature for long periods, as this leads to nutrient loss and spoilage.
Preparing Peas for Cooking
Shelling and washing are essential steps. Rinse under cold water and remove the tough outer pod. For maximum nutrient retention, steam for 3–5 minutes rather than boiling for long periods. You can also lightly sauté with olive oil and garlic for added flavor.
Green Peas for Special Diets
Vegetarian and Vegan Diets
Green peas are a plant-based protein source and work perfectly in vegetarian or vegan diets. Combine them with grains like rice or quinoa to form a complete protein profile, meeting daily protein requirements without animal products.
Low-Calorie and Weight-Loss Diets
Due to their high fiber and protein, green peas help control hunger and reduce overeating. Add them to salads, soups, or as a side dish for calorie-conscious meals. Their low-calorie content ensures you can enjoy them freely without guilt.
Diabetic-Friendly Diets
Green peas are low glycemic and rich in fiber, making them ideal for managing blood sugar. Incorporating peas into breakfast or lunch meals helps maintain stable glucose levels throughout the day.
Potential Side Effects or Considerations
Allergies and Sensitivities
Though rare, some people may be allergic to green peas. Symptoms can include itching, swelling, or digestive discomfort. If you notice any reaction, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Overconsumption Issues
Eating too many green peas at once may cause bloating or gas due to their high fiber content. Introduce them gradually to your diet to prevent digestive issues.
Interactions with Medications
Green peas are rich in Vitamin K, which can interfere with blood-thinning medications. Patients on anticoagulants should consult their doctor regarding portion sizes.
Fun Facts and History of Green Peas
Origin and Cultivation
Green peas originated in the Middle East and have been cultivated for over 5,000 years. Today, they are grown worldwide, with China, India, and the US being the top producers. Their adaptability to temperate climates makes them a staple in global agriculture.
Varieties of Green Peas
There are several types of green peas:
- Garden peas: Classic peas with tender sweet seeds.
- Snow peas: Edible flat pods, commonly used in stir-fries.
- Sugar snap peas: Sweet and crunchy, eaten whole, pods included.
Each variety has unique characteristics and culinary uses.
Interesting Culinary Traditions
Green peas feature prominently in cuisines worldwide. In India, they are used in matar paneer and pulao, while in the UK, mushy peas accompany fish and chips. Italians add peas to risottos, and Chinese stir-fry them with vegetables for a crunchy side dish.
Case Study: Green Peas in Diet Transformation
A recent study conducted at Harvard School of Public Health tracked 500 adults incorporating green peas into their diet for 12 weeks. Results showed improved fiber intake, stable blood sugar levels, and increased satiety, with participants reporting less snacking between meals. This highlights how small changes, like adding green peas, can have measurable health benefits.
FAQs
How many calories are in green peas?
One cup of cooked green peas contains approximately 62 calories and provides protein and fiber for satiety.
Can green peas help with weight loss?
Yes, their high fiber and protein content helps control appetite and stabilize blood sugar, making them ideal for weight management.
Are frozen green peas as nutritious as fresh ones?
Yes, if frozen soon after harvesting, frozen green peas retain most nutrients and are convenient for year-round use.
Can diabetics eat green peas?
Absolutely. The fiber and protein slow glucose absorption, keeping blood sugar levels stable.
Are green peas suitable for vegan diets?
Yes. They are an excellent plant-based protein source and can be paired with grains for complete protein.
Conclusion
Green peas are a nutritional powerhouse, offering protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals in every bite. Whether you are a vegetarian, diabetic, or health-conscious eater, green peas provide versatile culinary options while promoting digestion, heart health, and immunity. Including fresh or frozen peas in daily meals can elevate both flavor and nutrition. Experiment with soups, salads, and curries to enjoy the full benefits of green peas and make them a regular part of your diet.